Trigger
- Trigger is a JavaScript execution environment built on a Node.js container that can access resources on Circuit.
- In exaBase Studio, by utilizing the RxJS library, it is possible to receive external events via Entities, achieving high-level connectivity with other services and real-world events.
- It incorporates custom functions for monitoring Entities and kicking off Pipelines. Please utilize these built-in functions and methods along with sample codes.
Specifications
- Environment: Node.js (version updated appropriately to LTS)
- Related Libraries
| Library | Library Content | Requirement to Mention in Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| rxjs | Official library of RxJS. | Not required |
| context | Contains unique objects and functions for exaBase Studio. | Not required |
- Node Properties
| Property Name (* denotes required) | Property Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | You can set the name of the node. It can be freely written to avoid affecting deployment. | |
| ID* | Sets the name of the trigger that will also be reflected in the Blueprint. | |
| Description | You can write text that does not affect deployment. It is intended for describing the node. | |
| Entity default values | You can set initial values when monitoring connected Entities as Observables. | |
| Requirements | Add libraries you want to use in your code. | |
| Environment variables | You can set environment variables. It is designed for using secrets. When used, you can call them in the JavaScript code written in Trigger using process.env.{key}. | |
| Storage | A filesystem storage used for data persistence. Detailed information can be checked from Storage. | |
| Injection | A feature that allows files to be mounted to any path after the Node.js container is built. |
Context
- Context is an object for using the unique functions and features of exaBase Studio that are set by default in Trigger.
Reserved Variables
layerId
- Outputs the layer ID of the layered Circuit.
const {layerId} = context;
console.log(`layerId:${layerId}`);
Unique Functions in exaBase Studio
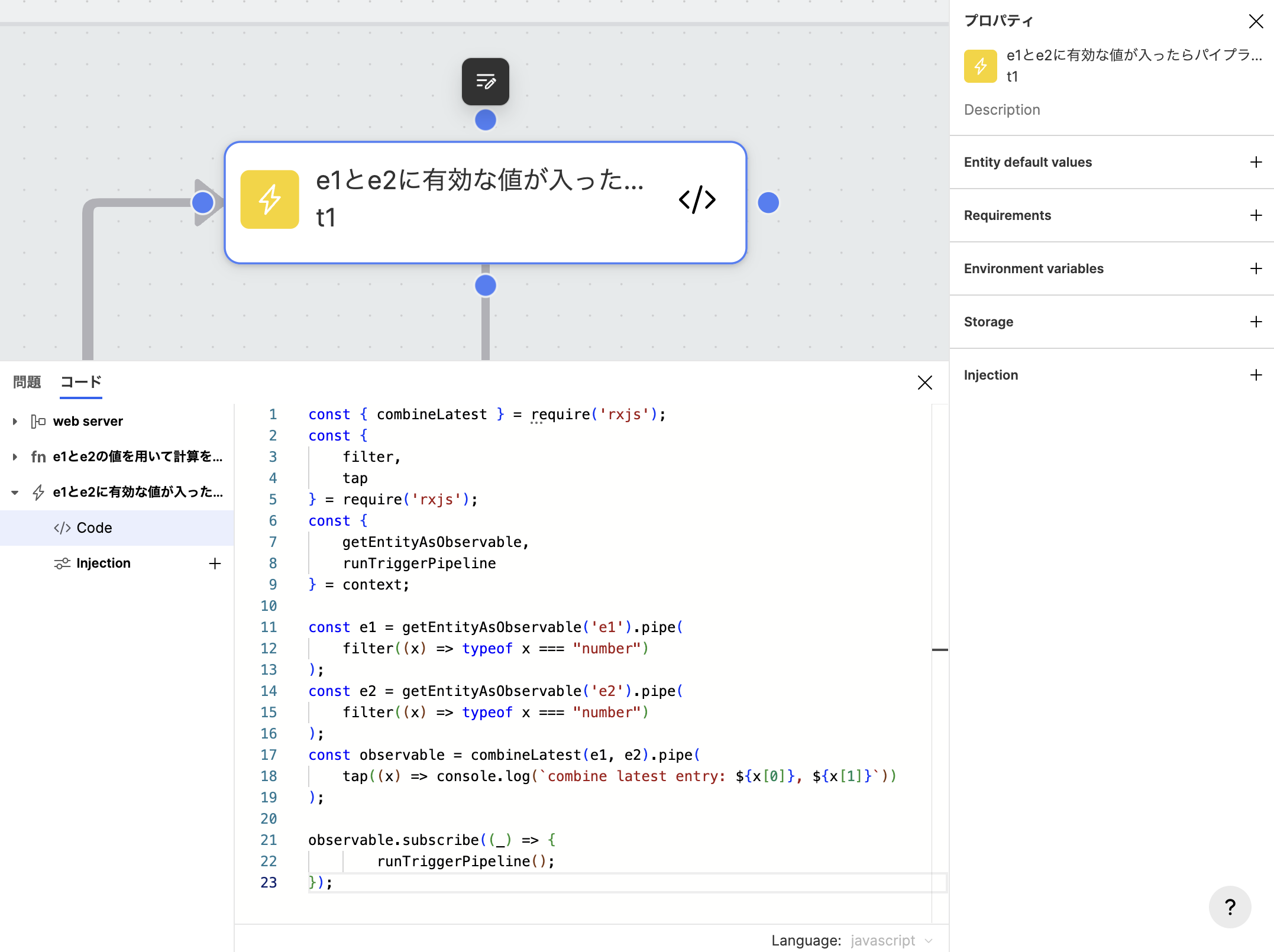
getEntityAsObservable()
- getEntityAsObservable can have Entities defined in the Blueprint as parameters.
- This function allows you to extract Entities as Observables, enabling you to handle them using commands in a reactive language.
- Extracting Entities as Observables means you can access and manipulate data streams.
Specifications
- Input the entity name as an argument.
- getEntityAsObservable("ENTITY NAME")
const e1 = getEntityAsObservable("e1");
runTriggerPipeline()
- runTriggerPipeline is a function to execute the pipeline connected to Trigger.
Example: Execute the pipeline when the value of Entity "e1" changes.
const {getEntityAsObservable, runTriggerPipeline} = context;
const { distinctUntilChanged } = require('rxjs/operators');
getEntityAsObservable("e1").pipe(
distinctUntilChanged()
)
.subscribe((_) => {
runTriggerPipeline();
});
Memory Management with Dispose
- Trigger subscribes to streams originating from data sources such as Entities.
- When dealing with stream data, if there is no appropriate way to deactivate the flow of data, these data can accumulate indefinitely, potentially causing memory leaks.
- To prevent this, it is crucial to manage data streams appropriately and unsubscribe (dispose) when they are no longer needed.
disposeBag
- The disposeBag object is a property of the context object and can be referenced with context.disposeBag.
- disposeBag holds the disposable objects returned when subscribing to Observables, and you can add the referenced streams to the disposeBag by using them as arguments in the putIn method.
Example: Register Entity "e1" as Observable and add it to the disposeBag.
const {disposeBag, getEntityAsObservable} = context;
const e1 = getEntityAsObservable("e1")
.subscribe(
console.log('subscription started')
)
.putIn(disposeBag);
disposing
- disposing is a property of the context object and can be utilized with context.disposing.
- You can register callback functions, such that in the following case, when dispose() is executed, console.log('disposing') acts as the callback function.
context.disposing = () => {
console.log(`disposing`);
};
dispose()
- Method to discard and perform post-processing on objects or items within the disposeBag.
Example: Dispose the context when the sum of Entity "e1" and "e2" (numeric data) exceeds 10.
combineLatest(e1, e2)
.pipe(
map((x) => x[0] + x[1]),
filter((x) => x >= 10)
)
.subscribe( (_) => {
console.log(`[layerId:${layerId}] dispose`);
dispose();
});